#219 Active Model
- Download:
- source codeProject Files in Zip (92.6 KB)
- mp4Full Size H.264 Video (12.7 MB)
- m4vSmaller H.264 Video (8.03 MB)
- webmFull Size VP8 Video (20.9 MB)
- ogvFull Size Theora Video (18.2 MB)
Episode 193 [watch, read] was all about tableless models. In that episode we created a model that used some of ActiveRecord’s features but which didn’t have a database table behind it. The technique we used was quite a hack as this is something that ActiveRecord wasn’t designed to do but now in Rails 3.0 we have a new feature called ActiveModel which makes doing something like this a lot easier.
Before we get into the details of ActiveModel we’ll first describe the part of the application that we’re going to modify to use it.
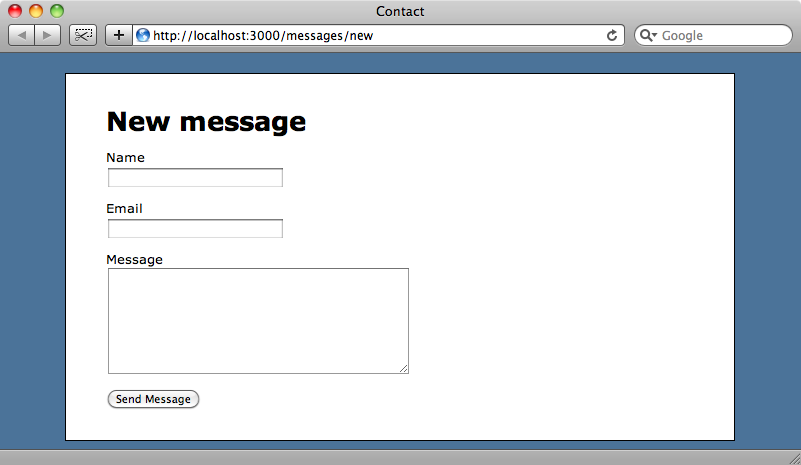
The screenshot above shows a contact form that has been created using Rails’ scaffolding. The application has a model called Message that is currently backed by ActiveRecord which means that we’re managing messages through the database. We’re going to change the way this form works so that it just sends emails and doesn’t store messages in a database table.
When you’re thinking of doing something like this it’s always a good idea to first consider your requirements and make sure that you really don’t want to store the data from the form in a database as there are often good side-effects to doing this. A database can act as a backup and also makes it easier to move the message-sending into a queue in a background process. For the purposes of this example, however, we don’t want any of that functionality so we’re free to go ahead and make our model tableless.
The code for the Message class looks like this:
class Message < ActiveRecord::Base validates_presence_of :name validates_format_of :email, :with => /^[-a-z0-9_+\.]+\@([-a-z0-9]+\.)+[a-z0-9]{2,4}$/i validates_length_of :content, :maximum => 500 end
Message inherits from ActiveRecord::Base as you would expect a model class to, but as we don’t want this model to have a database back-end we’re going to remove that inheritance. As soon as we do this, though, our form will no longer work as the validators are provided by ActiveRecord. Fortunately, we can restore this functionality by using ActiveModel.
If we take a look at the Rails 3 source code we’ll see the that there are activerecord and activemodel directories. The core Rails team has taken everything from ActiveRecord that wasn’t specific to the database backend and moved it out into ActiveModel. ActiveRecord still relies heavily on ActiveModel for the functionality that isn’t specific to the database and as ActiveModel is full-featured and thoroughly tested it’s great for use outside ActiveRecord.
It we take a look in the directory that contains the code for ActiveModel we can see the functionality that it provides.
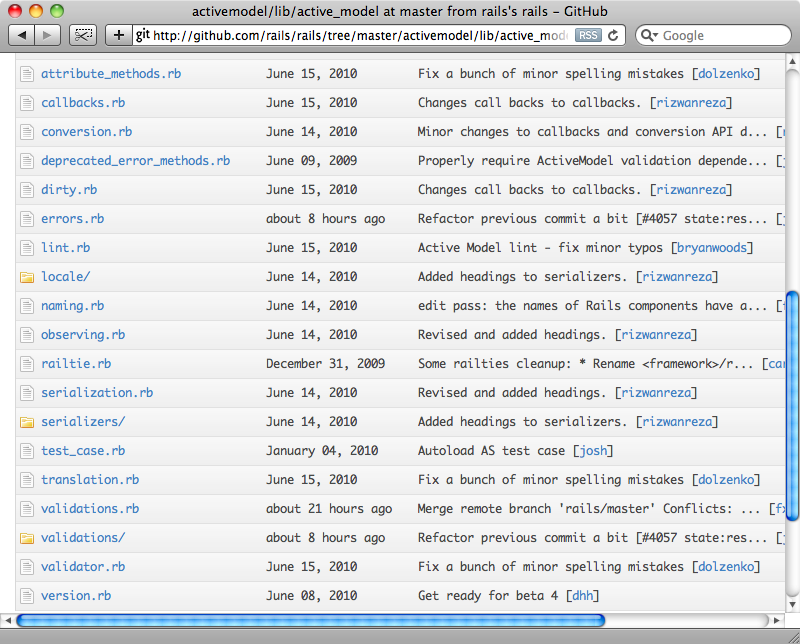
We can see from the list above that ActiveModel includes code to handle callbacks, dirty tracking, serialization and validation, among other things. The last of these is exactly what we’re looking for.
The code for validations has the following comment near the top and we can see from it that it’s fairly easy to add validations to a model. All we need to do is include the Validations module and provide getter methods for the attributes that we’re calling validators on.
# == Active Model Validations # # Provides a full validation framework to your objects. # # A minimal implementation could be: # # class Person # include ActiveModel::Validations # # attr_accessor :first_name, :last_name # # validates_each :first_name, :last_name do |record, attr, value| # record.errors.add attr, 'starts with z.' if value.to_s[0] == ?z # end # end #
Now that we know this we can apply it to our Message model.
class Message include ActiveModel::Validations attr_accessor :name, :email, :content validates_presence_of :name validates_format_of :email, :with => /^[-a-z0-9_+\.]+\@([-a-z0-9]+\.)+[a-z0-9]{2,4}$/i validates_length_of :content, :maximum => 500 end
This isn’t enough to get our model to behave as the controller expects it to, though. There are two problems in the create method. Firstly the call to Message.new won’t work as our Message model no longer has an initializer that takes a hash of attributes as an argument. Secondly, save won’t work as we don’t have a database backend to save the new message to.
class MessagesController < ApplicationController def new @message = Message.new end def create @message = Message.new(params[:message]) if @message.save # TODO send message here flash[:notice] = "Message sent! Thank you for contacting us." redirect_to root_url else render :action => 'new' end end end
We’ll fix the second of these problems first. While we can’t save a message we can check that it is valid, so we’ll replace @message.save with @message.valid?.
def create @message = Message.new(params[:message]) if @message.valid? # TODO send message here flash[:notice] = "Message sent! Thank you for contacting us." redirect_to root_url else render :action => 'new' end end
We can solve the first problem by writing an initialize method in the Message model that takes a hash as a parameter. This method will loop through each item in the hash and assign the value to the appropriate attribute for the message using the send method.
class Message include ActiveModel::Validations attr_accessor :name, :email, :content validates_presence_of :name validates_format_of :email, :with => /^[-a-z0-9_+\.]+\@([-a-z0-9]+\.)+[a-z0-9]{2,4}$/i validates_length_of :content, :maximum => 500 def initialize(attributes = {}) attributes.each do |name, value| send("#{name}=", value) end end end
If we reload the form now we’ll see that we’re not quite there yet, however.
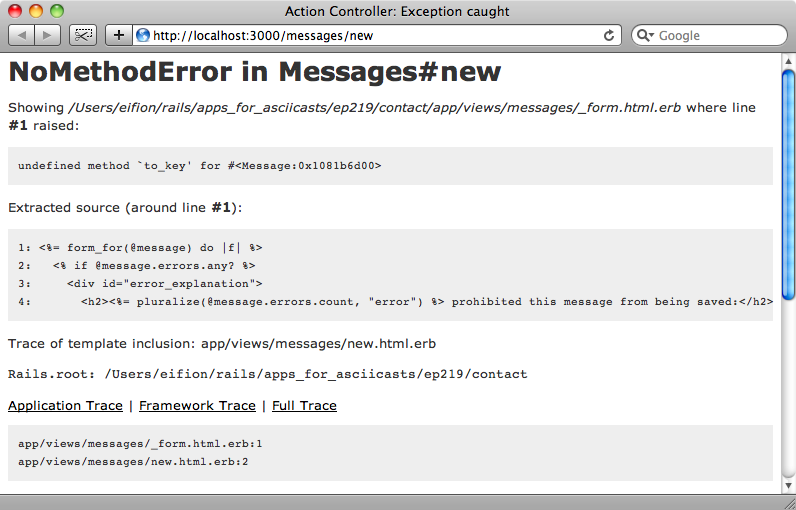
This time the error is caused by a missing to_key method in the Message model. The error is thrown by the form_for method so it seems that Rails itself is expecting our model to have functionality that it doesn’t yet support. Let’s add that functionality now.
Rather than guessing everything that Rails expects the model to have there’s a nice lint test included with ActiveModel that allows us to check whether our custom model behaves as Rails expects it to. If we include the ActiveModel::Lint::Tests module in a tests for the model it will check that the model has all of the required functionality.
The source code for the Lint::Tests module shows the methods that the model needs to respond to in order for it to work as it should, including to_key. We can make our model work by including a couple of ActiveRecord modules. The first of these is Conversion, which provides that to_key method and several others. The other module is the Naming module, but in this case we extend it in our class rather than including it as it includes some class methods.
As well as including the Conversion module we need to define a persisted? method in our model, which needs to return false as our model isn’t persisted to a database. With these changes in place our Message model now looks like this:
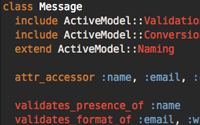
class Message include ActiveModel::Validations include ActiveModel::Conversion extend ActiveModel::Naming attr_accessor :name, :email, :content validates_presence_of :name validates_format_of :email, :with => /^[-a-z0-9_+\.]+\@([-a-z0-9]+\.)+[a-z0-9]{2,4}$/i validates_length_of :content, :maximum => 500 def initialize(attributes = {}) attributes.each do |name, value| send("#{name}=", value) end end def persisted? false end end
If we reload the form now it will work again which means that the Message model now satisfies all of the requirements that Rails 3 relies on for a model. If we try to submit the form we’ll see that the validators are working, too.
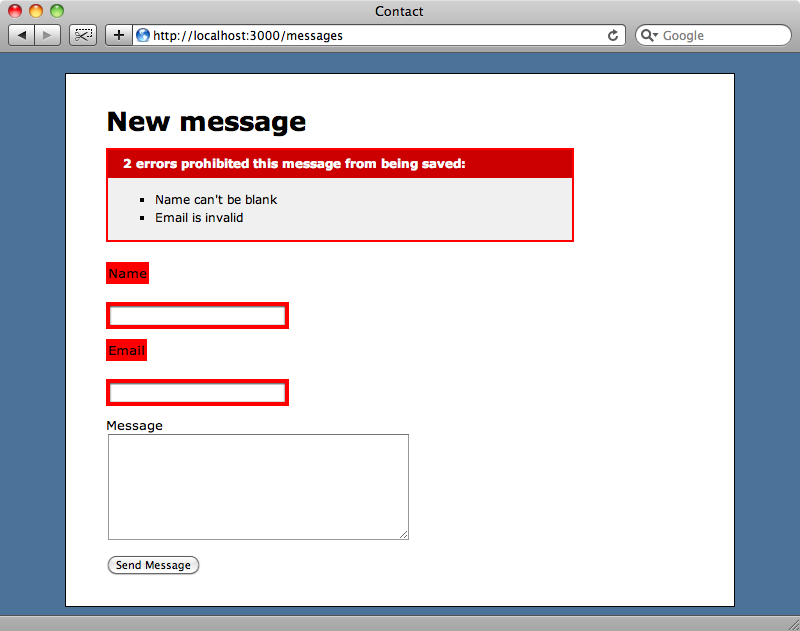
We’ve only covered a little of what ActiveModel provides in this episode but this should have been enough to whet your appetite and give you a reason to look more deeply into its source code to see what it can do. The code is well documented and structured so if you see something you might find useful then there should be enough information in the comments for that file to get you started using it.